You can calculate shareholders’ equity using the basic Accounting Equation https://www.pastgovernatori.org/opportunity-cost-definition-formula-example-and/ or the Investor’s Equation. Even though the financial models can be quite complex, the shareholder equity will fundamentally be calculated the same way. As a result, if dividends are paid, the shareholder equity value will decrease.
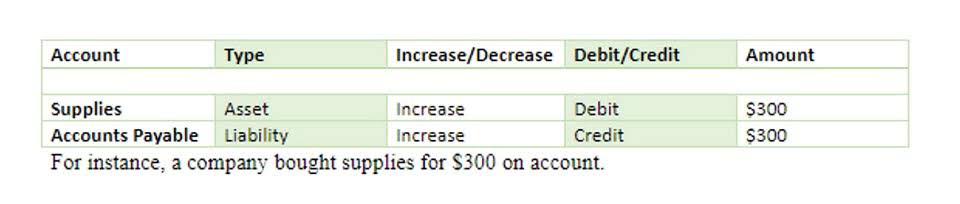
- The accounting equation is also known as the basic accounting equation or the balance sheet equation.
- As the calculation shows, the weighted-average number of shares of common stock for the year was 1,325.
- Valuation metrics such as the price-to-book (P/B) ratio incorporate common equity to gauge market perceptions and investor confidence.
- A statement of retained profits, which summarizes the changes in retained earnings for a given time period, is also kept.
- During a liquidation process, the value of physical assets is reduced, and there are other extraordinary conditions that make the two numbers incompatible.
- The accounting equation is a core principle in the double-entry bookkeeping system, wherein each transaction must affect at a bare minimum two of the three accounts, i.e. a debit and credit entry.
What Does Year-to-Date (YTD) Mean on a Payslip?
- In short, the asset value can be calculated by adding the firm’s equity and total debt or liabilities.
- After a 2-for-1 stock split, an individual investor who had owned 1,000 shares might be elated at the prospect of suddenly being the owner of 2,000 shares.
- Often referred to as paid-in capital, the “Common Stock” line item on the balance sheet consists of all contributions made by the company’s equity shareholders.
- Short-term debts generally fall into the current liabilities category, as these are things that a company is most likely to pay in the near future.
- Total equity and shareholders equity may not refer to the same thing.
The draws and dividends are not expenses and will not appear on the income statements. After the 25 shares of treasury stock are sold, the balance in Treasury Stock becomes a debit of $900 (45 shares at their cost of $20 per share). The Paid-in Capital from Treasury Stock now shows a credit balance of $170. Accumulated other comprehensive income refers to several items that were not included in net income and retained earnings. Examples include foreign currency translation adjustments and unrealized gains and losses on hedge/derivative financial instruments and postretirement benefit plans. Shareholders’ equity, as noted, is the total amount that a company could repay shareholders equity equation shareholders in the event of liquidation.
- Share capital or contributed capital represents the total financing or value received from the company’s shareholders in exchange for issuing common shares or preferred shares.
- A shareholder’s acquisition of firm stock over time also results in capital gains for them and grants them the ability to vote in board of directors elections.
- Shareholders’ equity, as noted, is the total amount that a company could repay shareholders in the event of liquidation.
- Stockholders’ equity is typically included on a company’s balance sheet but it’s possible to calculate it yourself.
Paid-in Capital or Contributed Capital

This is the sum that remains for the benefit of the company’s shareholders after all liabilities have been subtracted from the assets. The information used to determine the shareholders’ equity of company ABC Ltd. is presented above. The value of capital assets and property, including patents, structures, machinery, and notes receivable, are considered long-term assets.
What is common shareholders equity

When reviewing financial statements, information from shareholders equity is quite helpful. In liquidation situations, stock holders are paid last in line after debt holders. When a firm issues common shares and preferred shares in addition to its retained operating profits, this is referred to as shareholder equity, stockholder equity, or shareholder net worth. Retained earnings represent the cumulative net income of a corporation that has been retained rather than distributed to shareholders as dividends. These earnings are reinvested in the business to expand operations, purchase new equipment, or pay off debt.

- Non-current liabilities are debts that take longer to pay off (like bonds and deferred taxes).
- In other words, a 9% preferred stock with a par value of $50 being issued or traded in a market demanding 9% would sell for $50.
- Retained earnings represent the total amount of money generated by a company from its operations and not distributed to shareholders as dividends.
- Usually financial statements refer to the balance sheet, income statement, statement of comprehensive income, statement of cash flows, and statement of stockholders’ equity.
The long-term assets include fixed assets such as equipment, property, patents, etc. This is the value of funds that shareholders have invested in the company. When a company is first formed, shareholders will typically put in cash. Cash (an asset) rises by $10M, and Share Capital (an equity account) rises by $10M, balancing out the balance sheet. This account includes the total amount of long-term debt (excluding the current portion, if that account is present under current liabilities). This account is derived from the debt schedule, which outlines all of the company’s outstanding debt, the interest expense, and the principal repayment for every period.

Balance Sheet Equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity
On the other hand, if the market demands 8.9% and the stock is a 9% preferred stock with a par value of $50, then the stock will sell for slightly more than $50 as investors see an advantage in these shares. Stockholders’ equity is to a corporation what owner’s equity is to a sole proprietorship. Owners of a corporation are called Partnership Accounting stockholders (or shareholders), because they own (or hold) shares of the company’s stock. A company lists its treasury stock as a negative number in the equity section of its balance sheet. Treasury stock can also be referred to as “treasury shares” or “reacquired stock.”


